People often say that to start a business you just need a good idea and the rest will come on its own. However, as you progress, everything increases in difficulty and suddenly you are dealing with things you didn’t know about before and are trying to understand. For example, all the types of companies in Spain according to their legal form and knowing which one best suits your business model. But don’t worry, in this article we explain you everything about the types of companies that exist in Spain, come and join us!
Types of companies in Spain, an overview
If you are considering opening your own company in Spain, you have probably already been told about all the different types of companies you can open depending on your business model. It is also likely to have seemed overwhelming, as there are so many types of companies to choose from.
However, we believe that having an overview of the matter can help you to clarify things. Note, broadly speaking, companies can be classified into two groups according to their personality:
Individual, those owned by a single person, such as self-employed companies and private civil society.
Corporate, whose personality is totally different from that of its owners or partners. They must be registered in the Mercantile Registry and formalized through a public deed. For example, public civil companies, limited liability companies or cooperatives.
You may also be interested in: Opening license in Spain: how to obtain it?
Types of companies according to their legal status
It is important that you first understand that the legal form of a company is the legal modality that a company or professional chooses to carry out any economic activity. This affects its accounting and tax obligations, Social Security affiliation and its liability to third parties.
Thus, any individual or group of individuals who want to develop a business activity must choose the legal form that suits their business. It is appropriate to mention, in addition, that the legal form you choose will determine aspects such as:
Social Security affiliation.
Tax and accounting obligations.
Liability to third parties.
Initial investment.
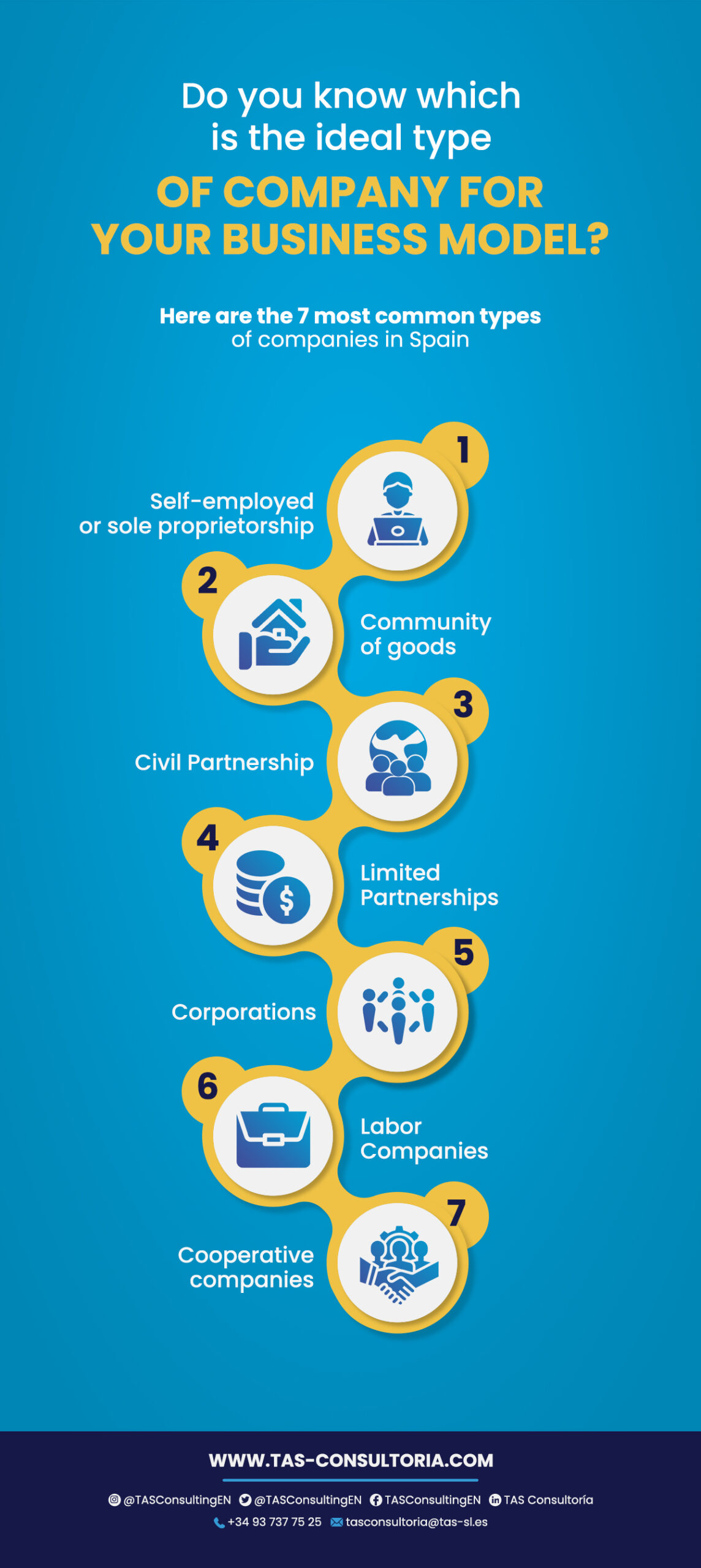
In this regard, the most common types of companies and partnerships in Spain are:
Self-employed or sole proprietor
This is the entrepreneur par excellence. The individual entrepreneur is the most widespread form of those who seek to take their first steps in their own business projects or create a company. Being oriented to initiatives that do not have very high capital, since it does not require a minimum amount of investment.
Among its advantages we can mention that, thanks to its reduced size, it is possible to manage it personally. Also, it means less administrative procedures and costs at the time of its incorporation, since the self-employed is not obliged to register its enterprise in the Commercial Registry.
Now, one of the biggest problems that this legal form represents is the “liability”, which is nothing more than the capacity to understand and answer for the actions of the company, third parties and debts with the past and future patrimony. Therefore, its liability is considered to be unlimited.
As for its taxation, it must be done through the IRPF, since the company’s profit is considered as individual. It is important to note that this tax is progressive, since the more profits the company receives, the higher the percentage to be taxed.
Community of property
This business model is one of the simplest legal forms of association between self-employed people who wish to carry out a common project. It is ideal for small individual entrepreneurs who have small businesses in mind.
It operates as a private agreement between at least two partners, who are called “co-owners” and who hold the ownership and title to an indivisible right or an asset for which a profit is obtained or expected to be obtained from the performance of a business activity.
This company model does not require a minimum initial capital and its incorporation is usually formalized through a private contract, without the need to be registered in the Commercial Registry. At the moment of contributing real estate or real rights, a public deed of incorporation would be executed before a notary public.
With this business model, the employee maintains his or her self-employed status and, as in the first case, must pay personal income tax.
Civil Society
The Civil Partnership is another ideal business model for self-employed entrepreneurs who want to start a small business for profit, together with other partners, and who do not need initial capital.
It is formalized through a private collaboration contract between two or more people who agree to contribute work (as industrial partners) and/or goods or money (as capital partners).
This type of company is subject to corporate income tax, unlike the previous cases, which are subject to personal income tax. However, as far as their liability is concerned, the partners have unlimited liability. This means that the company is liable for its actions, debts and before third parties with its past or future assets.
Limited partnerships
Limited companies have a mercantile nature, so their registration implies an act of incorporation. Of all the types of companies in Spain, this is the most common due to its nature.
As its name indicates, its partners are not personally or jointly and severally liable for corporate debts or third parties, since their liability is limited to the capital they contributed at the beginning.
For this type of company, there must be at least one founding partner who contributes 3,000 euros as initial capital, which will be divided into social participations and not into shares, as declared by other types of companies.
As far as your taxes are concerned, from 40,000 euros of profit, the taxes to be paid will be lower than those of a self-employed person and must be submitted to the Corporate Income Tax.
Corporations
Like the previous one, joint stock companies are the most used companies throughout Spain and are characterized by the fact that their capital is divided into shares that can be transferred freely, unlike limited companies.
It also accepts the participation of a large number of partners indicated in the bylaws and requires a minimum initial capital of 60,000 euros, being the model that requires the most invoices. This capital can be paid in all at once or partially paid.
For this model, liability is also limited to the initial capital contributed at the start. And, since this type of company is perfect for publicly traded businesses, it requires annual accounts and periodic inspections.
Lastly, corporations are required to file 25% of their profits received for corporate income tax purposes.
Worker-owned companies
The main characteristic of a labor company is its shares and the ownership of the company, dividing it into two different groups:
The labor class, which owns a minimum of 51% of the shares, and
The general class, which does not work directly in the company.
In this way, no partner has shares or partitions (depending on the structure chosen) that represent more than one third of the capital, thus avoiding absolute majorities.
In this sense, the capital contributed will be that corresponding to the type of company chosen, which may be 3,000 euros in the case of a limited liability company or 60,000 euros in the case of a public limited company.
Likewise, since it is a partnership, the liability of this type of company is also limited to the capital contributed by the partners. And, as in the previous case, the labor company is taxed for corporate income tax purposes at 25% of the profits it receives.
Cooperative societies
There is a lot to say about this type of company, but we will try to be brief. First of all, it is usually more common than in other surrounding countries, since it offers multiple benefits, and the number of companies that close is lower.
In this model, the liability is limited and at least 3 partners are required. However, in some autonomous communities, such as Andalusia, the minimum number of partners has been reduced to 2. It is all a matter of reviewing the regulations in force in the territory where the company is to be opened.
The profits received from this type of company are destined to cover the needs of the company and its operation, while the surplus is destined to the members. In addition, 30% of the surplus must be allocated to a mandatory reserve fund and to a specific reserve fund for promotional and educational activities.
This is due to the fact that cooperative societies carry out non-profit business activities for social purposes, which means that their purpose is the creation, improvement and maintenance of jobs for their members.
Also, it is worth mentioning that its liability is limited to the contribution of the partners. However, its bylaws may be amended to make it unlimited.
As far as taxation is concerned, unlike other types of companies in Spain, the cooperative society declares only 20% of the profits received before the Corporate Income Tax.
You may also be interested in: How to register a trade name in Spain?
Criteria for deciding which legal form best suits your business
Now that you know the types of companies in Spain according to their legal form, we will share with you six criteria that will help you choose the one that best suits your business model:
Consider the type of activity you will exercise, there are sectors such as banking or insurance that require a specific legal form.
The number of promoters will depend on the type of company you want to open. If you will be on your own, the autonomous company will be perfect for you, but if not, you can opt for some of the companies described above.
Take into account the initial economic investment that you will need, the incorporation of a company implies the contribution of 3,000 euros, while if you are self-employed, you will not need any.
Do not leave aside your liability to third parties when incorporating your company, discuss it with your partners and make the best decision.
Some legal forms, such as the self-employed, are subject to personal income tax, while others are subject to corporate income tax. Take into account the percentage of taxation, this will help you to make the best decision.
You should not neglect accounting obligations, which vary depending on the type of business you choose. The accounting of a self-employed person is (relatively) much simpler than that of a company, for example.
You may also be interested in: Corporate relationships in Spain: which one should I choose?
Now that you have all this information, there is only one thing left to decide: what is the type of company you want to open? If you want more information or need advice to find out which of all the types of companies in Spain is the one that best fits your business model, contact us through the TAS Consultancy website and make an appointment, our experts in situations like yours, will always be ready to help you.





Your email address will not be published .
Required fields are marked with *